Algorithmic Trading Guides
Algorithmic Trading Expression Logic
Master the logical expressions that power sophisticated automated trading systems and algorithms.
Logical expressions form the foundation of Investfly's algorithmic trading platform. These expressions define the precise conditions that trigger your automated trading decisions, including entry and exit signals for algorithmic trading strategies, advanced stock screeners, custom stock alerts, and automated trade orders. You'll build these powerful algorithmic trading expressions using our intuitive Expression Builder tool designed specifically for traders without coding experience.
Understanding Algorithmic Trading Expressions
An algorithmic trading expression is a mathematical statement that evaluates to either TRUE or FALSE, determining when your trading algorithm should execute a buy or sell action. Here are examples of effective trading algorithm expressions:
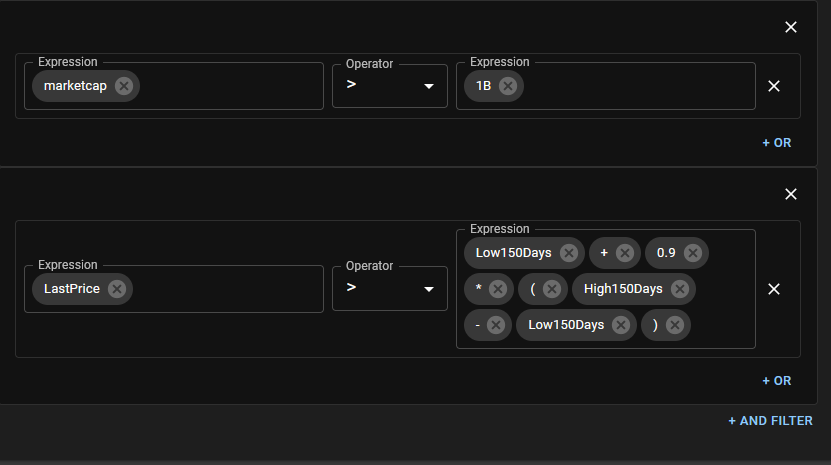
((marketcap > 1B)) && ((LastPrice < 1.1 * Low50Week))- Value stock strategy condition((AVGVOLUME > 1M)) && ((rsi5 > 70) || (rsi5 < 30))- Overbought/oversold momentum algorithm((( prev_uband_20_2 - prev_lband_20_2 ) / PrevPrice > ( uband_20_2 - lband_20_2 ) / LastPrice))- Bollinger band squeeze detection
All algorithmic trading expressions in Investfly's automated trading platform contain four essential elements:
Technical Indicator Variables
Examples: marketcap, prev_uband_20_2
Variables in your algorithmic trading expressions represent specific technical indicators and their parameters. Our automated trading platform automatically calculates these values in real-time as market data flows through your trading algorithm.
Trading Algorithm Constants
Examples: 30, 1.1
Constants are fixed numerical values that define thresholds and multipliers in your automated trading strategy. These remain unchanged during the evaluation of your algorithmic trading expressions.
Arithmetic Trading Operators
Examples: *, +, -, /
Arithmetic operators perform mathematical calculations within your algorithmic trading expression, allowing you to create complex formulas that combine multiple indicators and constants in your automated trading rules.
Logical Trading Operators
Examples: && (AND), || (OR)
Logical operators connect multiple conditions within your algorithmic trading strategy, enabling sophisticated decision trees in your automated trading system based on various market conditions occurring simultaneously.
When Investfly evaluates this expression, it inserts values for variables and evaluates it to either TRUE or FALSE.
Understanding Variables
Variables represent an indicator and associated parameters. When you define the variable, you map the variable to a particular indicator and corresponding parameters.
- A variable named rsi5 could represent indicator=RSI, period=5, bar = 1-minute bars.
- A variable named Low50Week could represent indicator=MIN, period=50, field=close, bar = 1-day bars.
You can use any variable name, but giving a meaningful name is recommended. The use of variables in the expression simplifies the expression because you can give a meaningful and short name to a combination of indicator and parameters.
Expressions in Stock Screeners
It is easiest to understand the use of expressions in the context of a stock screener. When you specify a logical expression in a stock screener, Investfly returns all stocks for which this logical expression evaluates to TRUE. In simpler words, this means it lists all stocks that meet the criteria represented by this logical expression.
For example, when an expression like rsi5 > 70 is evaluated, Investfly first maps the variable rsi5 to its full definition like [Indicator=RSI, period=5, bars=1-DAY]. Then, for each stock in the market, it computes the value for rsi5 based on historical bars, inserts the computed value in the expression, and finally evaluates the expression to TRUE or FALSE. All stocks for which the expression evaluates to TRUE are returned in the result set.
Expression Trigger Event
Another important concept to understand is the concept of an expression event. An event is triggered when a logical expression for a particular security transitions from FALSE to TRUE. By this definition, an event occurs at a specific point in time. After the event is triggered for a particular security, the expression has to transition from TRUE back to FALSE and again to TRUE for the subsequent event to occur.
The following table illustrates this:
| Time | Expression result | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 9:00:00 | FALSE | No |
| 9:00:01 | FALSE | No |
| 9:00:02 | TRUE | Yes, Event Triggered |
| 9:00:03 | TRUE | No |
| 9:00:04 | FALSE | No |
| 9:00:05 | FALSE | No |
| 9:00:06 | TRUE | Yes, Event Triggered |
Expressions in Automated Trading
When a logical expression is used to define criteria for a trade order, a trade signal is generated when the expression event is triggered by transitioning from FALSE to TRUE. For example, if you use EMA5 > EMA15 as a criterion, a trade event is generated exactly when EMA5 crosses over EMA15 in the price chart.
If EMA5 is already over EMA15, a trade signal is not generated at that time. For an expression event to trigger, EMA5 must drop below EMA15 and then rise over EMA15 again, thus triggering an event. The same mechanism is used to evaluate open trade conditions and close trade conditions in an automated trading strategy.
Next Steps
Now that you understand the basics of logical expressions, you're ready to learn how to build them using our Expression Builder. This tool provides a user-friendly interface for creating complex expressions without writing code.